Valiente Fm
Type Locality and Naming
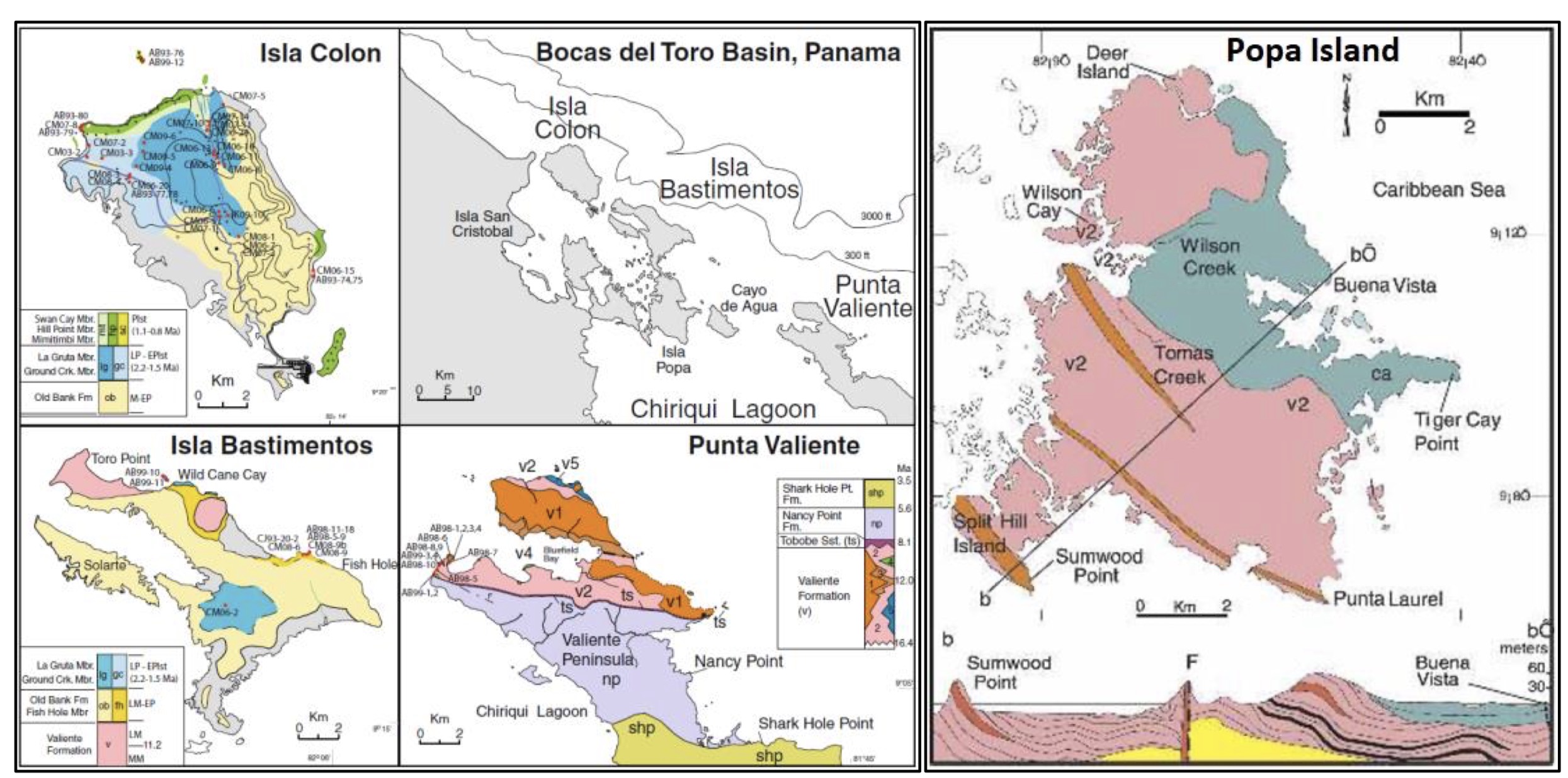
In the Southern Region of Bocas del Toro, the Valiente Fm crops out extensively on the Valiente Peninsula (Figure 1) and nearby Deer and Popa islands (Figure 2). In the Northern Region a spectacular exposure along the northwestern coast of Bastimentos Island (Figure 2) of columnar basalt and flow breccia are assigned to the Valiente Fm solely on their great similarity in lithology. The exposures range from Toro Point to the eastern side of Dreffe Beach and occur also at the western end of Long Beach. These basalt units probably form the basement of the entire Bocas del Toro Archipelago. Coates et al. (2005).
[Figure 1. Bocas del Toro archipelago, NW Panama with map of the western & central portion together with the geological maps of Isla Colon, Isla Bastimentos, Punta Valiente (Klaus et al. (2012)) and Popa Island (Coates et al. (2005)). Section (b-b’) over Popa Island shows the Valiente Fm where it is unconformably overlain by the Pliocene Cayo Agua Fm. On Popa Island, only the v1 basalt flow facies and the v2 coarse volcaniclastic facies (see Figure 043) (not associated with reef lenses) are present, with thin layers of low rank coal, an example of which is exposed along the coast immediately north of Punta Laurel. A prominent basalt dike is exposed at the tip of the Punta Laurel where it cuts the Valiente Fm.]
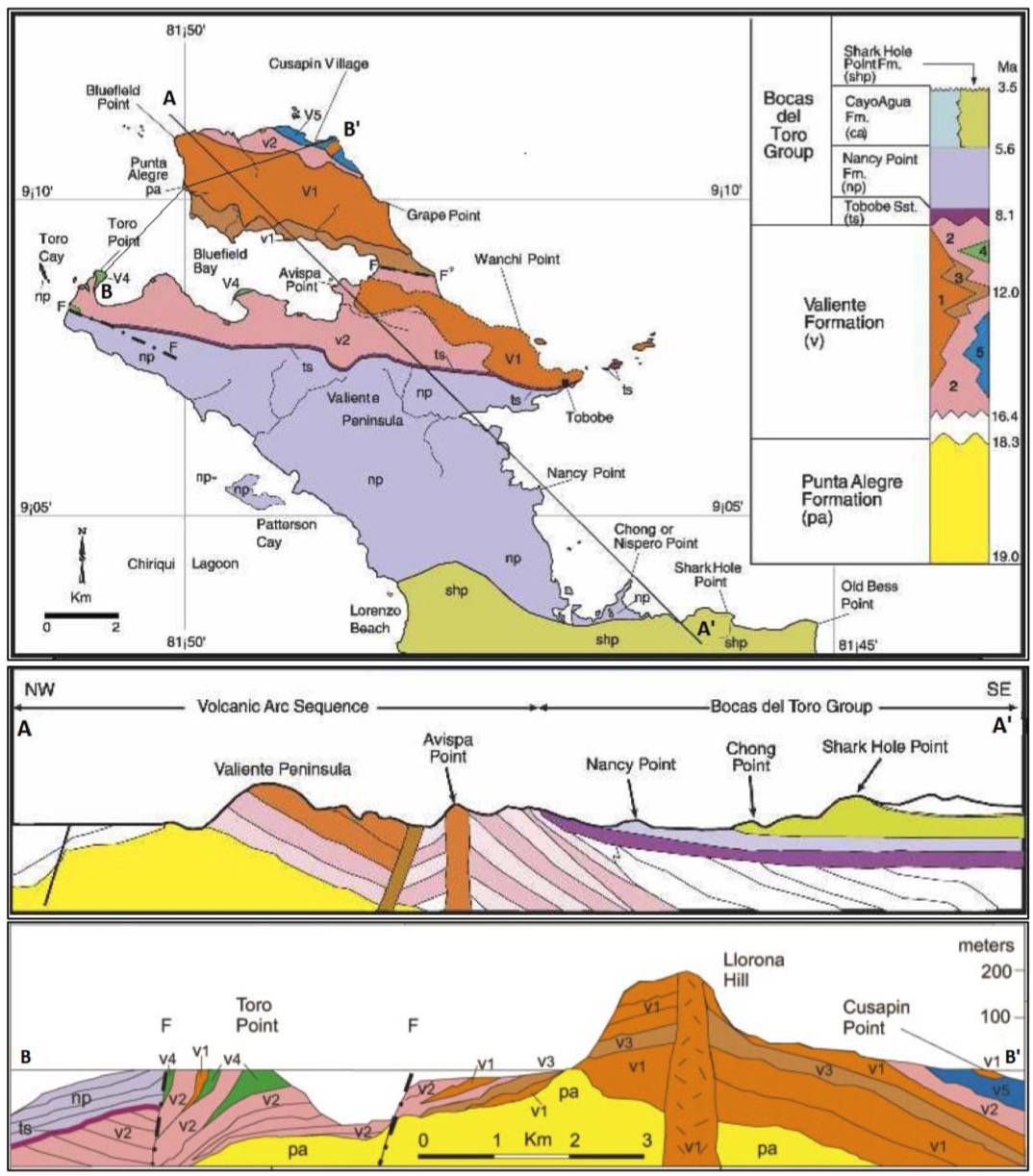
[Figure 2. Coates et al. (2003 & 2005)’s description of the geological map and cross sections (A-A’ and B-B’) of the Valiente Peninsula (Punta Valiente) showing the distribution of the Punta Alegre Fm and Valiente Fm and the Bocas Del Toro Gr. The five lithofacies of the Valiente Fm are indicated by separate colors and numbers on the key (upper right) as follows; v1) basalt lava and flow breccia facies; v2) coarse volcaniclastic facies; v3) pyroclastic facies; v4) coral reef facies; v5) marine debris flow and turbidite facies.]
Synonym: Punta Valiente Fm
Lithology and Thickness
(1) columnar basalt-lava and flow-breccia lithofacies,
(2) pyroclastic tuff (airborne volcanic ash deposits) lithofacies,
(3) coarse-grained volcaniclastic lithofacies (fluviatile/estuarine conglomerate),
(4) marine debris-flow and turbidite lithofacies,
(5) coral reef lithofacies (12 and 11 Ma; Klaus et al. (2012)
These facies intercalate and replace each other over very short distances, both laterally and vertically (for detailed descriptions of the facies, see Coates et al. (2003)). Figure 2 shows that the basalt lava and flow breccia facies form a core around which the other facies are distributed peripherally as terrestrial, coastal or marine slope deposits. Coates et al. (2005).
At Toro Point the coral reef lithofacies (5) consists of thick-bedded, rubbly, bioclastic, pale blue limestone that contains volcanic sand and silt grains in varying amounts. The limestone is ~37 m thick and has interbeds up to 6 m thick of volcanic-cobble conglomerate with well-rounded clasts and a graywacke matrix. Klaus et al. (2012).
Thickness: 135 m thick at the type section at Toro Point, Valiente Peninsula (Figure 1; Figure 2). Klaus et al. (2012)
[Figure 3. (C) Typical basaltic flow breccia in the stratotype of the Valiente Fm, along the coast, 900 m south of Toro Point, Valiente Peninsula (Figure 043; Figure 042), Bocas del Toro. (D) Coarse-grained volcaniclastic facies in the stratotype of the Valiente Fm, along the coast ;850 m south of Toro Point, Valiente Peninsula, Bocas del Toro. (E) Bedded reef-rubble limestone in the stratotype of the Valiente Fm at Toro Point, Valiente Peninsula, Bocas del Toro. (F) Overturned block of the turbidite lithofacies of the Valiente Fm, 1 km south of Toro Point, Valiente Peninsula, Bocas del Toro. In the photographs with a hammer for scale, the hammer head is 14 cm long and the handle is 34 cm long. Coates et al. (2003).]
Relationships and Distribution
Lower contact
Upper contact
Regional extent
GeoJSON
Fossils
Planktonic microbiotas and radiometrically dated basalt in the sequence indicate that the Valiente Fm ranges in age from 16.5-11.5 million years old and includes marine deposits from near-shore to as deep as 1000 m, as well as several types of terrestrial deposits. Coates et al. (2003).
Age
Depositional setting
Additional Information
References: Landau et al. (2012b); Coates et al. (2003 & 2005); Klaus et al. (2012)